Payment Facilitator vs Payment Gateway | What's the Difference?
- 20 min read
- 15 april 2024
Online payments have really changed the way we shop and do business, making things super convenient and fast. But, you know, with the ease of clicking to purchase, it's vital to ensure safe transactions. That's where payment facilitators (PayFacs) and payment gateways come in. They're not just there to process transactions; think of them as your fraud protectors. Understanding the advantages of payment facilitator vs payment gateway it's key to running your business smoothly. This knowledge can boost efficiency and help you find the right payment solution that fits your business perfectly. In this article, we'll explore both of them in-depth, explain their differences, and show how picking the right one can push your business ahead. Let's dive into it!
Understanding the Basics: How does Payment Processing Work?
Behind every online purchase, a complex algorithm of technology and finance occurs in seconds, ensuring that money safely transfers from buyer to seller. This process, known as payment processing, involves several key players, including:
- Merchants: These are sellers, businesses, or service providers that sell goods or services. They start the process by providing a platform (such as a website or POS system) for customers to make payments.
- Acquiring Bank: This financial institution manages credit card transactions for merchants, helping transfer funds from customers' banks.
- Payment Gateway: This technology acts as a bridge, securely transmitting the customer's payment information to the payment processor, encrypting the sensitive card data, and verifying its authenticity.
- Payment Processors: These companies operate in the background to handle the technical aspects of processing transactions, such as authorizing, capturing, and settling payments.
- Payment Facilitators (PayFacs): They simplify the whole payment process, especially for smaller merchants. They handle payments under a main merchant account, making the merchant account sign-up process easier and more efficient.
Let's explore further how all the pieces come together - what role do payment gateways play and how do payment facilitators assist in this process?
What is Payment Gateway?
In simple terms, a payment gateway is a digital tool that connects a customer's online shopping cart to the payment processor receiving payment from the credit or debit card. If we were to break down its role into simpler terms, it would look something like this:
- Collection: The starting point of any online transaction. As the customer finalizes a purchase, the gateway collects all necessary payment details, acting as the first responder in the chain of payment processing.
- Encryption: Here, the gateway transforms the payment data into a secure, encrypted format. This ensures that sensitive information remains confidential, safeguarding it against potential cyber threats.
- Authorization: Then the encrypted data is sent to the payment processor, which works with the bank to check if the transaction is valid and to ensure funds are available.
- Confirmation: When the bank approves the transaction, the payment gateway notifies both the customer and the merchant to finalize the transaction.

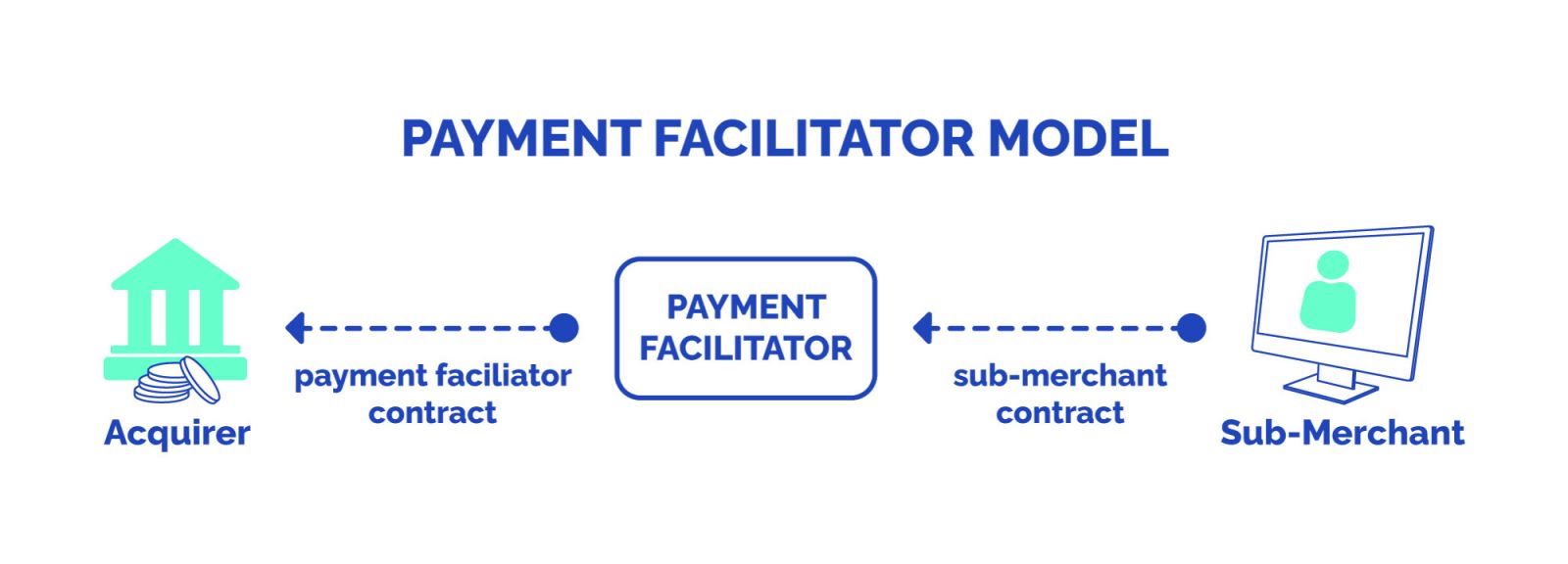
What is a Payment Facilitator?
A payment facilitator acts as a partner between small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) and the often complex world of online transactions. They simplify the process of accepting electronic payments, allowing businesses to focus on their core operations. They eliminate the need for individual merchants to go through the process of getting a merchant account directly from a bank or credit card company. Instead, businesses can join by signing up under the master merchant account of the payment facilitator. This approved account brings together transactions from different sub-merchants (the businesses using the PayFac service).
Key features of the payment facilitators include:
- Faster Merchant Onboarding: Payment facilitators take care of the work involved in setting up and verifying accounts. This process helps businesses start operating quickly, enabling them to secure merchant accounts relatively fast.
- Diverse Payment Options: They usually connect you to many payment options. That means you can take credit cards, debit cards, cool digital wallets like Apple Pay and Google Pay, and set up recurring payments. Having all these choices helps businesses meet their customers' needs and stops buyers from leaving items in their online carts just because of limited payment options.
- Enhanced Security Measures: Payment facilitators play a crucial role in protecting sensitive financial data. By following strict Payment Card Industry Data Security Standards (PCI DSS) and implementing strong security measures, they ensure the protection of customer information.
- Simplified Reconciliation and Reporting: Handling transactions and balancing accounts can take up a lot of time for small businesses. Payment facilitators usually have easy-to-use dashboards that give you combined reports on all transactions. This simplifies the process of balancing accounts and gives you useful information on sales patterns and customer habits.
Payment Facilitator vs Payment Gateway? Exploring the Differences
Payment facilitators and payment gateways both play key roles in helping businesses process payments effectively. However, they have distinct functions and advantages. It's important for businesses to understand these differences to select the best fit for their needs.
|
Feature |
Payment Facilitator |
Payment Gateway |
|
Primary function |
Acts as an intermediary, managing all aspects of payment processing. |
Securely transfers payment data from the merchant to the processor. |
|
Merchant Account Requirement |
Not required |
Required |
|
Processing volume Limitation |
$1 million/ year. If more, need to onboarding with an acquirer. |
No limitation, as connected with acquirers. |
|
Setup Process and Time |
Fast onboarding |
Longer due to merchant account requirements |
|
Payment Methods Supported |
Wide range, varies by provider |
Wide range, varies by provider |
|
Access to Funds |
May be delayed |
Often quicker |
|
Customization Options |
Less flexibility |
High flexibility |
|
Fees and Pricing Structures |
Percentage per transaction, additional fees |
Varied, may include setup costs |
Primary Function: Payment facilitators primarily serve as intermediaries that simplify the entire payment process for businesses, not only processing payments but also handling compliance and security measures. Payment gateways, in contrast, focus specifically on securely transfering payment information from the point of sale to the payment processor.
Merchant Account Requirement: One key difference is the need for a merchant account. PayFacs usually don't ask individual businesses to get their own merchant accounts; they work under the PayFac's main merchant account. In contrast, payment gateways need businesses to have a separate merchant account for transaction processing.
Setup Process and Time: Payment facilitators provide a quick setup process, allowing businesses to start processing payments quickly. On the other hand, setting up a payment gateway can be more time-consuming due to the need for a merchant account and integration complexities.
Payment Methods Supported: Both platforms generally support a wide array of payment methods, including credit cards and digital wallets. However, the range and types of supported payment methods can vary based on the provider.
Access to Funds: With payment facilitators, access to funds might be delayed as they go through the facilitator's account first. On the flip side, payment gateways, which connect directly to a merchant's account, could provide faster access to funds.
Customization Options: Payment gateways often allow for higher customization levels to seamlessly integrate into a business's checkout process. Payment facilitators might provide standardized solutions that are less flexible when it comes to customization.
Fees and Pricing Structures: Payment facilitators generally charge a percentage per transaction, which might include additional fees. Payment Gateways have very varied pricing structures, including payment processing fees, monthly fees, and sometimes setup costs.
Payment Gateway vs Payment Facilitator? Pros and Cons
Now let's take a closer look at the advantages and disadvantages of each payment processing option.
Pros of Using a Payment Facilitator
Opting for a payment facilitator can greatly benefit businesses, especially those looking for a quick market entry. Key advantages include:
- Ease of Setup: Businesses can start accepting payments almost immediately, bypassing the approval processes associated with opening traditional merchant accounts.
- Simplified Operations: They handle the complexities of payment processing, compliance, and security.
- Broad Payment Method Support: They typically support a wide array of payment methods, appealing to a diverse customer base.
Cons of Using a Payment Facilitator
Despite their appeal, PayFacs might not suit every business model. Some drawbacks are:
- Costs: Though convenient, the fees might be higher compared to having a direct merchant account, especially for businesses processing large transaction volumes.
- Standardized Solutions: Customization options are limited, which might not satisfy all business needs.
- Delayed Fund Access: Funds might take longer to reach the business’s account due to intermediary processing.
- Risk of Account Holds or Termination: PayFacs keep a close eye on transactions to spot any fraudulent activity. This attention to detail might mean that funds are sometimes held or accounts could be closed if they consider the business's transactions too risky.
- Dependency on the Facilitator: Many businesses depend a lot on their PayFac for handling transactions. This reliance can become a weak spot if the PayFac goes down, changes its policies, or increases its fees.
- Volume Limitation: For businesses working under a PayFac, there's a key detail to keep in mind: the limit on how much you can process annually is set at $1 million. If your transactions go beyond this, you'll need to directly connect with an Acquirer.
Pros of Using a Payment Gateway
Payment gateways are great for businesses that want to manage their payment processes directly. Benefits include:
- Customization and Integration: They provide a wide range of customization options, ensuring a smooth integration with the company's current systems.
- Direct Transactions: Businesses benefit from faster access to funds, which helps improve cash flow management.
- Scalability: Gateways can accommodate higher transaction volumes as your business grows.
- Enhanced Security: Compliance with PCI DSS and additional security measures protect against fraud.
Cons of Using a Payment Gateway
However, payment gateways come with challenges:
- Thorough Setup: Requiring a merchant account and integrating it takes up additional time and resources.
- Cost Variability: Fees can differ quite a bit, with setup fees, monthly charges, and transaction costs, which can make budgeting a bit tricky.
Each option presents a unique blend of benefits and limitations. Businesses must weigh these factors carefully, considering their specific needs, resources, and long-term goals.
Which Solution is the Best for Your Business?
When you're deciding between a payment facilitator vs payment gateway, it's important to consider key factors that can affect your business's efficiency and customer satisfaction. Here's what you should think about:
- Business Size and Needs: Start-ups and new businesses often prefer payment facilitators for their quick setup and user-friendly interface, which helps streamline transactions. On the other hand, established companies dealing with higher transaction volumes tend to opt for payment gateways due to their scalability and reliability. It’s good to consider that sub-merchants under a PayFac model face a processing cap of $1M annually; exceeding this requires transitioning to a direct agreement with an Acquirer.
- Payment Methods You Want to Offer: Expanding the ways customers can pay can really boost their satisfaction. If your customers have particular payment preferences, make sure your system can handle them. Payment facilitators usually offer a wide variety of payment options right from the start, while payment gateways might need some extra setup to support specific methods.
- Level of Control and Customization Desired: Tailoring your checkout payment page to match your brand is crucial. If you value customization, a payment gateway provides greater flexibility. On the other hand, for businesses seeking a straightforward, ready-to-use option, a payment facilitator could be the ideal choice.
- Budget Limitations: When deciding, think about the costs involved with each choice. Payment facilitators usually have a fixed fee per transaction, which could be higher but easier to predict. Payment gateways might have lower transaction fees, but keep in mind extra expenses like monthly charges, setup fees, or costs for added services.
- Control and Dependency: Consider how much control you want over your account and funds. Using a payment facilitator often means less control and a higher dependency on the provider for managing your transactions, which could pose a risk if the facilitator faces issues or changes their policy. Businesses that prioritize independence might find a payment gateway more suitable, as it generally offers more control over the payment process and funds management.
Make sure the choice you make fits what your business needs now and in the future as it grows. Choose the option that gives you the right mix of features, cost-effectiveness, and user experience designed for your customers' requirements.
Conclusion
Wrapping it up, when it comes to choosing between payment facilitators and gateways, it all boils down to making a strategic decision tailored to your business's unique journey. Payment facilitators provide a smooth entry into the market without the hassle of complex setups, which is ideal for startups and small businesses. On the other hand, payment gateways offer a solid foundation for businesses seeking customization and direct control over financial transactions, which is especially beneficial for larger companies with broad operations and high transaction volumes.
Equipped with a deep understanding of these key differences and applications, you are now in a great position to select a payment processing partner that not only caters to today's needs but also evolves with the challenges of tomorrow. Keep in mind that the best choice is one that fits seamlessly with your business model, supports your growth, and enhances your customers' satisfaction.
Need help deciding which option is best for your business?
Contact us today for expert advice on optimizing your payment processing and growing your business.
FAQ
What is the difference between a payment facilitator, a payment processor, and a payment gateway?
A payment facilitator makes it easier for businesses to sign up for a merchant account by providing them with a sub-merchant account linked to their main one. A payment processor, on the other hand, is the backbone of the transaction process, handling the details of credit card transactions between buyers, sellers, and financial institutions. Finally, a payment gateway acts as a secure intermediary, encrypting and transmitting payment data from the customer to the acquirer and then returning transaction details or approval to the seller.
What is the difference between a payment facilitator and a payment aggregator?
While both offer merchant services under a master account, a payment facilitator assumes greater responsibility for managing the relationship with the sub-merchants, including control over underwriting and compliance. In contrast, a payment aggregator, also known as a third-party processor, gathers funds from various transactions before settling them, focusing less on direct merchant relationships and more on the aggregation and processing of transactions.
What is the difference between a payment gateway and a payment provider?
A payment gateway helps to securely transfer transaction data between a merchant's website and the acquiring bank or payment processor. On the other hand, a payment provider offers a broader range of services. They usually include a payment gateway as part of their package, along with payment processing, merchant accounts, and sometimes even point-of-sale systems. Essentially, they act as a means of payment onvenient one-stop solution for all a merchant's payment requirements.
Can both payment facilitators and payment gateways support international transactions?
Yes, both payment facilitators and payment gateways can support international transactions, but they differ in their capabilities. Payment facilitators offer a simple setup for global payments with limited customization. On the other hand, payment gateways provide more flexibility in terms of currency support and localization options, but they may require additional setup or integration for full international payment support.